Parotid Surgery
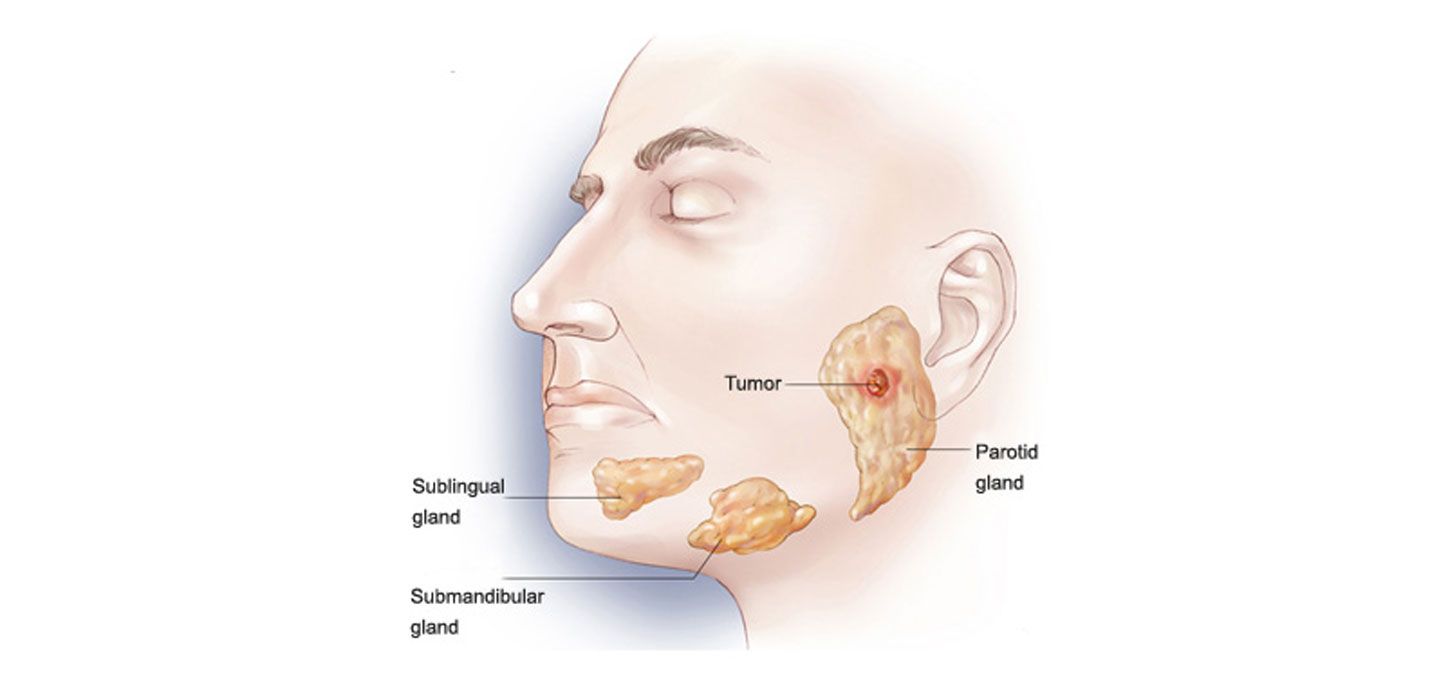
What is the Parotid?
The parotid is the largest of three paired major salivary glands and is located just anterior and inferior to the ear. Along with the submandibular and sublingual glands, the two other paired major salivary glands, they produce and secrete saliva into the oral cavity.
The parotid, and indeed any of the other major salivary glands can become swollen for a number of reasons, most common amongst them from viral or bacterial infections, stone formation and inflammation. The above conditions are often transient and benign, and will resolve in most instances with medical treatment, except for parotid stones which may require surgical removal.
The parotid gland may also develop tumors or neoplasms. These typically present as a painless neck lump located over the angle of the jaw or just under the earlobe. Tumors may also arise from the submandibular and sublingual glands (located below the jaw-line and under the tongue respectively), but these are less common than those of the parotid gland.
Assessment
Evaluation of a parotid tumor usually requires a diagnostic scan, either a CT or MRI, and a fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB). These investigations provide us with a good assessment of whether the tumors are likely benign or malignant with about an 80 – 90% accuracy. While the majority of parotid tumors, between 75 – 80% of them are benign, 40 - 50% of submandibular gland tumors are malignant. For this reason, in addition to the fact that benign tumors will continue to grow over time and a small fraction of them can turn cancerous over many years, most parotid and submandibular tumors are recommended surgery.
Parotid Surgery / Modified Facelift Approach
The most common surgical procedure for removal of a parotid tumor is a SUPERFICIAL PAROTIDECTOMY, so called because it removes the entire superficial lobe of the parotid gland with the tumor complete.
Parotid surgery is a major operation, and is particularly important because removal of the parotid gland requires careful and meticulous dissection and preservation of the facial nerve. The facial nerve is an important nerve that exits the skull base, traverses through the substance of the parotid and divides into five or more delicate branches that supply the muscles of facial animation. These muscles affect functions like eyelid closure, frowning, smiling and blowing. The plane of the facial nerve and its branches divides the parotid gland into superficial and deep lobes, and as most tumors are located within the superficial lobe, a superficial parotidectomy is the appropriate surgical procedure. The risk of permanent damage to the facial nerve is less than 1% when surgery is performed by an experienced parotid surgeon. In situations where the tumor is located in the deep lobe of the parotid, both the superficial and deep lobes are removed, a procedure called a TOTAL PAROTIDECTOMY, performed again with careful preservation of the facial nerve and all its peripheral branches.
Typically surgery on the parotid gland is performed through a fairly large incision that starts from the upper ear and curves gently down to the lower neck, called a modified Blair incision. The reason for this traditionally large incision is to be able to carefully identify and dissect out the facial nerve from its point of exit in the skull base through the gland.
More recently, a much more aesthetically pleasing incision, called a modified facelift incision, has been developed to remove parotid tumors. This incision starts in the upper ear as well, but curves around the ear lobe behind the ear, to continue into the hairline instead of down the neck. This incision is practically imperceptible after complete healing, and therefore much more pleasing to the patient. Although patients do have to be carefully selected for this approach, we routinely perform a modified facelift incision for most patients requiring parotid surgery.
Recovery from parotid surgery is quick. Patients are typically discharged a day or two after surgery with normal speech and swallowing, facial nerve function and complete independent mobility with minimal postoperative pain
- Trusted Singapore Thyroid and Head & Neck Surgeon
- More Than 20 Years’ Experience
- Surgical Expertise in Thyroid Nodules & Cancer
- Personalised Care & Best Practices
- Evidence Based Treatment Options
(Stanford University, USA)
3 Mount Elizabeth #17-07
Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre
Singapore 228510
